HOW MANY INDEPENDENT FILMS GET A THEATRICAL RELEASE?
 For many independent filmmakers, whether or not their film reaches the big screen means everything. No matter the money to be made via television deals or the massive audiences possible with VOD, a theatrical release is where it’s at.
For many independent filmmakers, whether or not their film reaches the big screen means everything. No matter the money to be made via television deals or the massive audiences possible with VOD, a theatrical release is where it’s at.
Therefore, we thought it would be helpful to look at how many films actually make it to theaters. We built a dataset of all United States-produced narrative (non-documentary) feature films which were shot in 2017 and looked at their distribution outcome.
Before we get into the details, we need to be a little bit careful about our definition of a “theatrical release”. For example, it isn’t really fair to compare a film that plays for a group of friends and family in a theater rented by the director to a three-month theatrical engagement.
We therefore split films into four possible outcomes (in all cases, we’re talking about the “Domestic” market, aka the United States and Canada).
- No theatrical release – These films had no commercial theatrical release domestically. They may have had a premiere in a theater, and played in film festivals, but they never announced a theatrical release for paying customers.
- Nominal release – These films officially have theatrical release dates but no box office figures have been reported, meaning that it was very likely to have been an extremely small release, possibly in just one or two theaters.
- Small release – Films which grossed between $1 and $100k at the domestic box office.
- Large release – Films which grossed over $100k at the domestic box office.
We also excluded 123 films made in 2017 and subsequently released by one of the major studios, so we’re looking only at independent films in this analysis.
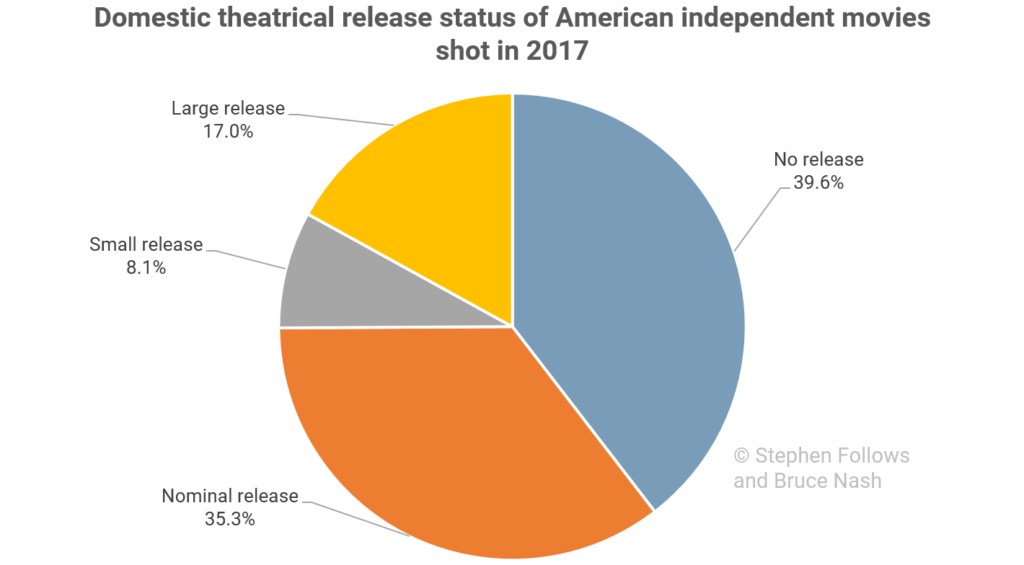
This revealed that 40% of independent films made in 2017 did not get any kind of theatrical release.
A further 35% had a nominal release, with no reported box office; 8% grossed between $1 and $100k; and 17% grossed over $100k. Out of the 877 independent films, 220 reported earnings at the box office, which is a shade over 25%.
Common sense dictates that independent film-makers should have a back-up plan for a home market release for their film. That said, we wanted to see if different genres might be more or less likely to get that coveted place in theaters.
How Different Are The Release Outcomes For Films Of Differing Genres?
It turns out that genre plays quite a big role in the type of release a film will get.
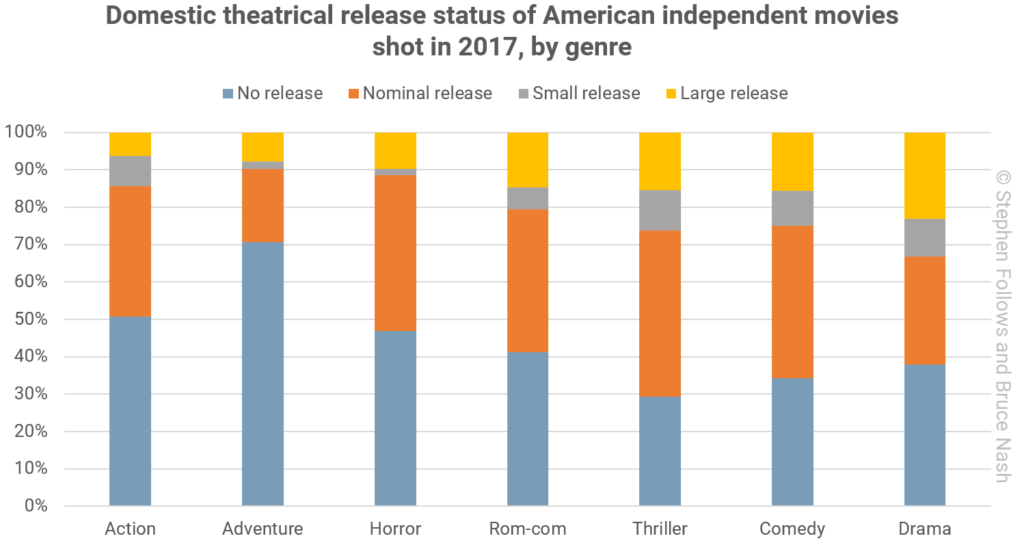
Among the films most likely to get no release at all are ones we classify as adventures. These tend to be family-friendly films that involve a certain amount of action, but no real peril – films with names like Camp Cool Kids and Sweet Sweet Summertime. They are often made for TV, or go directly to DVD or a streaming platform. In all, 71% of independent adventure films don’t play in theaters. The second and third most likely films not to play in theaters are the classic “genre films”: action and horror, at 51% and 47% respectively.
The films most likely to get a nominal release are thrillers, at 45%, followed by horror (42%) and comedy (41%). As we mentioned earlier, a nominal release implies that getting reviews (hopefully good ones!) will help the financial fortunes of a film. So it makes sense that the films with nominal releases are the ones that would benefit from good reviews.
Small releases are dominated by dramas, comedies, and thrillers. 11% of thrillers, 10% of dramas, and 9% of comedies get a small release. These are films that were probably hoping to get good word of mouth and decent earnings from theaters, but maybe just fell short.
Finally, large releases are the realm of the drama, with 23% of independent dramas earning over $100,000 at the domestic box office. Comedies (16%) and thrillers (15%) are also more likely to get into this top tier.
We don’t know why, but romantic comedies don’t really stand out one way or another in this analysis: their release profile is almost exactly the same as for the market as a whole. We don’t perhaps think of romantic comedies as the typical film, but they have typical distribution chances.
How Does Having A Pre-Existing Audience Correlate With A Theatrical Release?
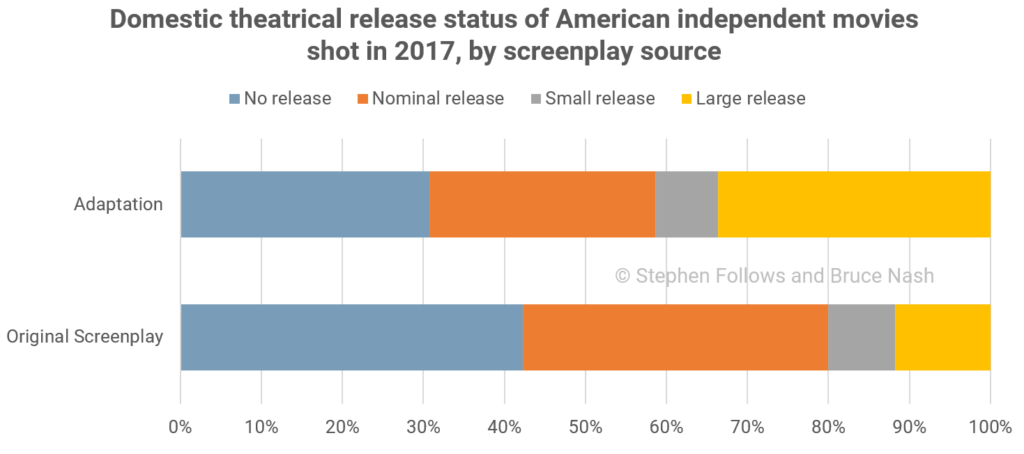
Studio-produced films are much more likely to be adaptations than independent films, for a number of reasons (such as studios having deeper pockets and needing to secure bigger crowds to break even). Overall, about half of studio-produced films are based on pre-existing material.
Although rarer, there are still a lot of independent films that are adaptations of one sort or another. Over 200 of the films in our dataset, or 24% of the independent films, are not original screenplays. Most of these are based on real-life events or books, but there’s a wide range of sources used in independent films including short films, web series, games, toys, musicals, religious texts, and plays, among others.
These adaptations are three times as likely to secure a large theatrical release compared to independent films with original screenplays. That’s a significant jump, and shows how hard it is for an independent film based on original material to get a substantial theatrical release. As we’ve shown in a previous article, to get into this top bracket, an original film needs to be of the highest quality. In general, as one would expect, distributors are much more likely to put resources behind a film that they know has an existing audience.
Conclusion
Seeing a film played in a theater is still regarded as the best way to experience the art form. It’s also, understandably, the goal of many film producers. By looking at a complete set of films made in a single year, we can see how likely it is that a given film will realize that dream, and it turns out that there’s actually a pretty good chance a film will play to a paying audience at some point, if that’s what the film-maker sets out to do.
However, the numbers say that an independent film will, five times out of six, not go on to make much money in theaters. Knowing how to maximize revenue from the home market remains an essential skill for an independent producer.
Notes
All the films studied today are feature films shot in the United States, or made by US-based production companies, and completed in 2017. It’s possible that some of these films have not yet reached theaters, and so in the fullness of time the figures may change slightly. That said, we are conducting this research in mid-August 2019 and so the vast majority of films have either reached theaters or never will.
About the Authors
Stephen Follows is a writer, producer and film industry analyst. His film research has been featured in the New York Times, The Times, The Telegraph, The Guardian, The Daily Mail, The Mirror, The Evening Standard, Newsweek, The New Statesman, AV Club and Indiewire. He acted as an industry consultant and guest on the BBC Radio 4 series The Business of Film, which topped the iTunes podcast chart, and has consulted for a wide variety of clients, including the Smithsonian in Washington. In addition to film analytics, Stephen is an award-winning writer-producer and runs a production company based in Somerset House, London.
Bruce Nash is the founder and President of Nash Information Services, LLC, the premier provider of movie industry data and research services and operator of The Numbers, a website that provides box office and video sales tracking, and daily industry news. Mr. Nash founded the company in 1997 and it now serves approximately 1,000 clients, from the major studios to first-time independent filmmakers. Mr. Nash provides regular commentary and analysis for media outlets, including the L.A. Times, the New York Times, Variety, the Wall Street Journal, 60 Minutes, and CBS News. Mr. Nash is the official adjudicator of movie records for the Guinness Book of Records. To learn more about his company’s services, visit Nash Information Services.
Copyright © 2021 Stephen Follows and Bruce Nash. All rights reserved. Reproduced with permission.
Explore more articles and research at Producers Resources.